Severe osteomyelitis remission with intraosseous CDS
Case Report: Successful Remission of Severe Osteomyelitis with Intraosseous Application of CDS
by COMUSAV
Abstract
This case report discusses the successful treatment of a middle-aged male patient with severe osteomyelitis following an open bone fracture. The patient faced the prospect of amputation due to non-healing of the fracture. However, a novel treatment involving the intraosseous injection of 500 ppm CDI (chlorine dioxide) in saline solution led to remarkable recovery.
Introduction
Osteomyelitis is a challenging condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the bone. Traditional treatments often involve prolonged antibiotic therapy and, in severe cases, amputation. This report details a unique approach utilizing intraosseous CDS administration as a potential alternative treatment, highlighting its efficacy and safety.
Case Presentation
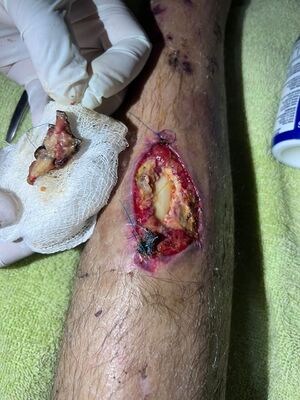
Patient Information
- Age: Middle-aged male
- Medical History: Open bone fracture resulting in severe osteomyelitis
- Initial Condition: Non-healing fracture, significant pain, and risk of limb amputation
Treatment Plan
The medical team assessed the patient's condition and proposed amputation as the only viable option. However, the leading physician suggested an alternative approach using intraosseous CDS treatment. After thorough discussion, the patient provided written consent for this experimental treatment.
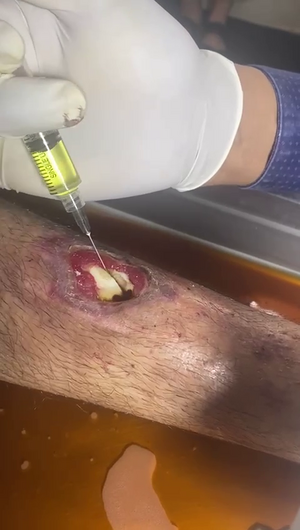
Intraosseous CDS Administration
- Substance Used: 500 ppm CDI in saline solution
- Method: Direct injection into the bone marrow
Protocol C 20
The patient was also placed on Protocol C 20 to enhance treatment outcomes.
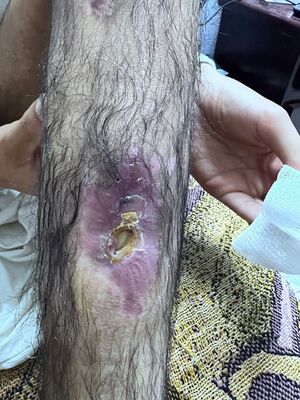
Results
The intraosseous CDS injection resulted in:
- Rapid Recovery: Noticeable improvement within weeks
- Total Remission: Complete healing of the fracture with no signs of osteomyelitis
- No Adverse Effects: The patient tolerated the treatment well with no reported side effects
The medical team observed an astonishing response to the treatment, leading to the avoidance of amputation. The patient expressed satisfaction with the results, and the attending physician noted significant changes in the patient's condition.
Discussion
This case presents a promising alternative for treating severe osteomyelitis through intraosseous CDS injection. Colleagues were left baffled by the rapid recovery and absence of complications. This case underscores the need for further research to validate the effectiveness of CDS in similar clinical scenarios.
Conclusion
The intraosseous administration of CDS represents a novel and effective treatment modality for severe osteomyelitis. This case encourages further investigation into its use, potentially providing a viable alternative to more invasive surgical options such as amputation.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the medical team for their support and the patient for consenting to this innovative treatment approach.
Images
Images showcasing pre-treatment and post-treatment conditions may be attached here.
This report serves as a basis for future studies and clinical trials to explore the potential applications of intraosseous CDS treatments in osteomyelitis and other bone-related infections.
