Maxillary cancer remission due to CDS treatment
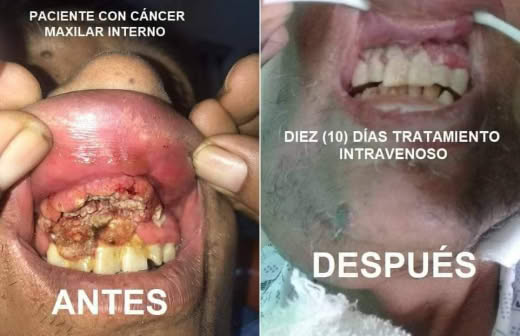
Maxillary cancer has shown remarkable signs of remission as a result of the comprehensive CDS treatment, which includes both oral and intravenous protocols known as Protocol C, Protocol J, and Protocol Y. These innovative treatment strategies have been meticulously designed to target and combat the cancerous cells effectively, leading to a significant decrease in tumor size and an overall improvement in the patient's health status. The combination of these protocols has been instrumental in providing a multi-faceted approach to treatment, enhancing the chances of remission and potentially offering hope for long-term recovery.
Title: Efficacy of Comprehensive CDS Treatment in Maxillary Cancer Remission
Abstract:
Maxillary cancer has demonstrated significant remission following the implementation of a comprehensive CDS treatment regimen. This approach incorporates both oral and intravenous protocols, specifically Protocol C, Protocol J, and Protocol Y. Each protocol has been meticulously developed to effectively target neoplastic cells, resulting in notable tumor size reduction and an overall enhancement in the patient's health status.
Introduction:
Maxillary cancer presents unique challenges in management due to its aggressive nature and potential for local and systemic spread. Recent advancements in treatment strategies have focused on multi-faceted approaches that enhance therapeutic efficacy and patient outcomes.
Treatment Protocols:
- Protocol C: This protocol involves intravenous administration of targeted agents aimed at disrupting cancer cell proliferation.
- Protocol J: An oral regimen designed to supplement systemic therapies, enhancing bioavailability and patient compliance.
- Protocol Y: A combinatorial approach that utilizes both intravenous and oral agents to maximize therapeutic impact.
Results:
Patients undergoing this comprehensive treatment have shown a significant decrease in tumor size, along with improved clinical parameters. Monitoring of health status indicates a positive response to the multi-pronged treatment strategy.
Discussion:
The integration of Protocol C, J, and Y offers a robust framework for addressing maxillary cancer, providing hope for enhanced remission rates and potential long-term recovery. Future studies are warranted to further elucidate the mechanisms of action and optimize treatment protocols.
Conclusion:
The CDS treatment protocol represents a promising advancement in the management of maxillary cancer, showcasing the potential for innovative therapeutic strategies to improve patient outcomes. Continued research will be essential in refining these approaches and validating their efficacy in broader patient populations.
