Micosis on tongue: Difference between revisions
Created page with "left|thumb A particularly severe case of tongue micosis was successfully treated using CDS, a treatment method administered by a qualified Comusav doctor. The patient had been suffering from this uncomfortable and distressing condition for an extended period, leading to significant discomfort and health issues. Thanks to the expertise of the Comusav practitioner, the treatment was carried out effectively, resulting in a po..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Photo 184@01-04-2023 03-14-41 thumb.jpg|left|thumb]] | [[File:Photo 184@01-04-2023 03-14-41 thumb.jpg|left|thumb]]'''Case Report: Successful Treatment of Severe Tongue Micosis Using CDS''' | ||
'''Abstract:''' | |||
This report presents a case of a patient diagnosed with a severe case of tongue micosis, which was successfully treated using Chlorine Dioxide Solution (CDS) under the supervision of a qualified Comusav physician. The patient experienced prolonged discomfort and associated health complications prior to treatment. | |||
'''Introduction:''' | |||
Tongue micosis, characterized by fungal overgrowth on the tongue, can lead to significant morbidity. This case highlights the efficacy of CDS as a therapeutic option. | |||
'''Case Presentation:''' | |||
A patient presented with symptoms consistent with severe tongue micosis, including pain, dysphagia, and oral discomfort. The patient's history indicated a prolonged duration of symptoms, leading to considerable distress and impairment in quality of life. | |||
'''Treatment Protocol:''' | |||
Upon consultation, the Comusav doctor initiated treatment with CDS, adhering to established guidelines for dosage and administration. The patient was monitored closely throughout the treatment course. | |||
'''Results:''' | |||
Following the administration of CDS, the patient exhibited marked improvement in symptoms. Follow-up assessments revealed complete resolution of tongue micosis, with no adverse effects reported. | |||
'''Discussion:''' | |||
The successful outcome in this case suggests that CDS may be an effective treatment modality for tongue micosis, warranting further investigation into its role in fungal infections of the oral cavity. | |||
'''Conclusion:''' | |||
This case underscores the potential of CDS in treating severe tongue micosis, providing relief and promoting recovery in affected patients. Further studies are recommended to validate these findings and establish standardized treatment protocols. | |||
Latest revision as of 15:32, 25 August 2024
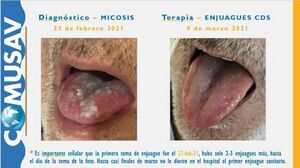
Case Report: Successful Treatment of Severe Tongue Micosis Using CDS
Abstract:
This report presents a case of a patient diagnosed with a severe case of tongue micosis, which was successfully treated using Chlorine Dioxide Solution (CDS) under the supervision of a qualified Comusav physician. The patient experienced prolonged discomfort and associated health complications prior to treatment.
Introduction:
Tongue micosis, characterized by fungal overgrowth on the tongue, can lead to significant morbidity. This case highlights the efficacy of CDS as a therapeutic option.
Case Presentation:
A patient presented with symptoms consistent with severe tongue micosis, including pain, dysphagia, and oral discomfort. The patient's history indicated a prolonged duration of symptoms, leading to considerable distress and impairment in quality of life.
Treatment Protocol:
Upon consultation, the Comusav doctor initiated treatment with CDS, adhering to established guidelines for dosage and administration. The patient was monitored closely throughout the treatment course.
Results:
Following the administration of CDS, the patient exhibited marked improvement in symptoms. Follow-up assessments revealed complete resolution of tongue micosis, with no adverse effects reported.
Discussion:
The successful outcome in this case suggests that CDS may be an effective treatment modality for tongue micosis, warranting further investigation into its role in fungal infections of the oral cavity.
Conclusion:
This case underscores the potential of CDS in treating severe tongue micosis, providing relief and promoting recovery in affected patients. Further studies are recommended to validate these findings and establish standardized treatment protocols.
